개요
한국의 수학 교육과정 상 고등학교 때 배우게 되는 삼각형 및 삼각함수에 관한 정리. 사인 법칙과 함께 삼각형의 변의 길이와 각의 크기를 찾을 때 유용한 정리이다. 한국에서는 이상하게도 제 1 코사인 법칙, 제 2 코사인 법칙의 두가지로 나누는데, 세계적으로 코사인 법칙이라 하면 제 2 코사인 법칙만을 가르킨다. 사실 제 1 코사인 법칙은 법칙이라 하기에는 조금 민망하다.
제 1 코사인 법칙
“ 1. [math]\displaystyle{ a=b\cos C+c\cos B }[/math]
2. [math]\displaystyle{ b=c\cos A+a\cos C }[/math]
3. [math]\displaystyle{ c=a\cos B+b\cos A }[/math]“
증명
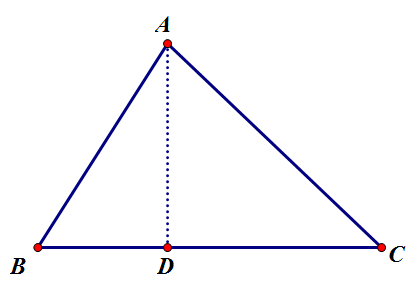
[math]\displaystyle{ \triangle{ABC} }[/math]의 꼭짓점 [math]\displaystyle{ A }[/math]에서 대변 [math]\displaystyle{ \overline{BC} }[/math](혹은 그 연장선) 에 내린 수선의 발을 점 [math]\displaystyle{ D }[/math]라 하자.
1. [math]\displaystyle{ \triangle{ABC} }[/math]가 예각삼각형:
[math]\displaystyle{ a=\overline{BD}+\overline{CD}=c\cos B+b\cos C }[/math]
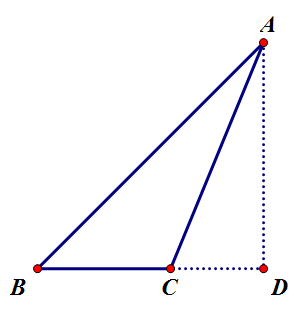
2. [math]\displaystyle{ \triangle{ABC} }[/math]가 둔각삼각형:
[math]\displaystyle{ a=\overline{BD}-\overline{CD}=c\cos B-b\cos\left(180^{\circ}-C\right)=c\cos C+b\cos C }[/math]
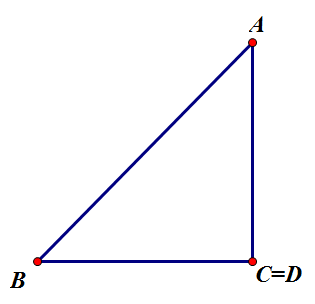
3. [math]\displaystyle{ \triangle{ABC} }[/math]가 직각삼각형:
[math]\displaystyle{ a=\overline{BD}=c\cos B }[/math]. 한편, [math]\displaystyle{ \angle C=90^{\circ} }[/math]이므로, [math]\displaystyle{ \cos C=0 }[/math]. [math]\displaystyle{ \therefore a=c\cos B+b\cos C }[/math]
나머지 세 변에 대해서도 같은 방법으로 증명이 가능하다.
제 2 코사인 법칙
“ 1. [math]\displaystyle{ a^2=b^2+c^2-2bc\cos A }[/math]
2. [math]\displaystyle{ b^2=c^2+a^2-2ca\cos B }[/math]
3. [math]\displaystyle{ c^2=a^2+b^2-2ab\cos C }[/math]“
증명
제 1 코사인 법칙으로부터 유도가 가능하다. 1번 식에 [math]\displaystyle{ a }[/math]를 곱하면
[math]\displaystyle{ a^2=ab\cos C+ac\cos B\quad\cdots4 }[/math].
2번 식에 [math]\displaystyle{ b }[/math]를 곱하면
[math]\displaystyle{ b^2=bc\cos A+ab\cos C\quad\cdots5 }[/math].
3번 식에 [math]\displaystyle{ c }[/math]를 곱하면
[math]\displaystyle{ c^2=ac\cos B+bc\cos A\quad\cdots6 }[/math].
이제 4-5-6을 해주면, [math]\displaystyle{ a^2-b^2-c^2=ab\cos C+ac\cos B-bc\cos A-ab\cos C-ac\cos B-bc\cos A=-2bc\cos A }[/math]이고, 정리해주면 [math]\displaystyle{ a^2=b^2+c^2-2bc\cos A }[/math]. 나머지 두 식도 비슷한 방법으로 증명이 가능하다.
활용
두 변과 그 끼인각을 알 때 나머지 한 변의 길이를 이 공식을 사용해서 알 수 있다. 혹은 코사인 값만 한 쪽에 둔 뒤 나머지 값을 전부 다른 쪽으로 몰아주면 [math]\displaystyle{ \cos A=\frac{b^2+c^2-a^2}{2bc} }[/math]가 되는데, 이는 세 변의 길이를 알 때 각의 크기를 구하는 데에 쓰인다. 혹시 눈치 챈 사람이 있을진 모르지만, 위 두 조건은 삼각형의 결정 조건이다. 즉, 삼각형에서 제 2 코사인 법칙의 두 식은[* 원식과 그 변형] 해가 반드시 하나이다.[* 원식은 양수값과 음수값 두개가 나오지만 변의 길이는 무조건 양수이므로 해가 하나, 변형식은 코사인함수가 [math]\displaystyle{ 0^{\circ} }[/math]와 [math]\displaystyle{ 180^{\circ} }[/math]사이에선 일대일 대응이기 때문에 해가 하나이다.] 값에 따라서 해가 2개 나올 수도 있는 사인 법칙과는 구분되는 점. 또한 제 2 코사인 법칙을 잘 보면 알겠지만, 피타고라스 정리의 일반화라고 할 수 있다.