한국의 수학 교육과정상 고등학교 때 배우게 되는 평면기하학의 공식 중 하나. 삼각형에서 변의 길이와 각의 크기를 알 때, 나머지 모르는 변의 길이와 각의 크기를 삼각함수를 이용해서 구할 수 있게 해준다. 자세한 내용은 아래와 같다.
“ [math]\displaystyle{ \triangle{ABC} }[/math]의 세 각의 크기 [math]\displaystyle{ \angle A,\angle B,\angle C }[/math]와 세 변의 길이 [math]\displaystyle{ a,b,c }[/math](각 각의 대변), 그리고 외접원의 반지름의 길이 [math]\displaystyle{ R }[/math]에 대해 [math]\displaystyle{ \frac{a}{\sin A}=\frac{b}{\sin B}=\frac{c}{\sin C}=2R }[/math]이 성립한다. “
증명[편집 | 원본 편집]
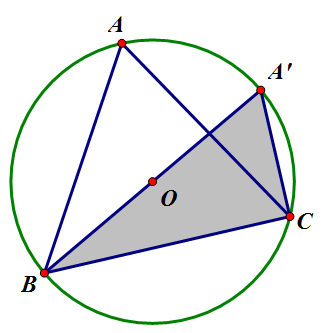
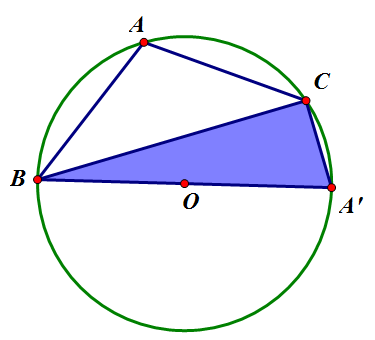
[math]\displaystyle{ \triangle{ABC} }[/math]의 외접원의 중심을 [math]\displaystyle{ O }[/math]라고 하고, [math]\displaystyle{ \overline{BO} }[/math]의 연장선이 원과 만나는 점을 [math]\displaystyle{ A' }[/math]라 하자. 그럼 [math]\displaystyle{ \overline{BA'} }[/math]은 외접원의 지름이므로, [math]\displaystyle{ \overline{BA'}=2R }[/math]이다.
1. [math]\displaystyle{ \triangle{ABC} }[/math]가 예각삼각형 일 때:
위 그림에서, [math]\displaystyle{ \angle A=\angle A' }[/math]이고[1], [math]\displaystyle{ \angle{BCA'}=90^{\circ} }[/math]이다.[2] 따라서, [math]\displaystyle{ \sin A=\sin A'=\frac{a}{2R} }[/math]이고, 정리하면 [math]\displaystyle{ \frac{a}{\sin A}=2R }[/math].
2. [math]\displaystyle{ \triangle{ABC} }[/math]가 둔각삼각형 일 때:
위 그림에서, [math]\displaystyle{ \angle A=180^{\circ}-\angle A' }[/math]이고,[3] [math]\displaystyle{ \angle{BCA'}=90^{\circ} }[/math]이다. 따라서, [math]\displaystyle{ \sin A=\sin{180^{\circ}-A'}=\sin A'=\frac{a}{2R} }[/math]이고, 정리하면 [math]\displaystyle{ \frac{a}{\sin A}=2R }[/math].
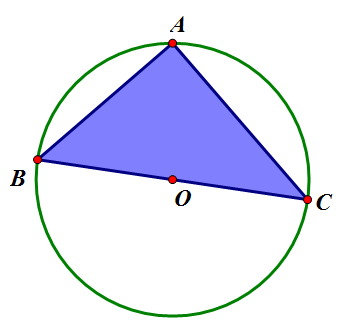
3. [math]\displaystyle{ \triangle{ABC} }[/math]가 직각삼각형 일 때:
위 그림에서, [math]\displaystyle{ \angle A=90^{\circ} }[/math]이다. 따라서, [math]\displaystyle{ \sin A=1,\,a=2R }[/math]이므로, [math]\displaystyle{ \frac{a}{\sin A}=2R }[/math]이 성립한다.
각 [math]\displaystyle{ \angle B,\angle C }[/math]에 대해서도 같은 방법으로 증명할 수 있다. [math]\displaystyle{ \therefore\,\frac{a}{\sin A}=\frac{b}{\sin B}=\frac{c}{\sin C}=2R }[/math].
활용[편집 | 원본 편집]
1. 각을 변으로 바꾸기: [math]\displaystyle{ \sin A=\frac{a}{2R},\,\sin B=\frac{b}{2R},\,\sin C=\frac{c}{2R} }[/math]
2. 변을 각으로 바꾸기: [math]\displaystyle{ a=2R\sin A,\,b=2R\sin B,\,c=2R\sin C }[/math]
3. 변의 비와 각의 비: [math]\displaystyle{ a:b:c=\sin A:\sin B:\sin C }[/math]
삼각형에서 삼각함수의 등식을 증명하거나 넓이를 찾을 때에는 위 세 가지 변형과 코사인 법칙을 잘 활용하면 쉽게 해결할 수 있다.