(그래프 이미지 추가 + 표 가운데 정렬) |
잔글편집 요약 없음 |
||
| 7번째 줄: | 7번째 줄: | ||
== 종류 == | == 종류 == | ||
사실 정다면체는 다섯 가지밖에 없다. | 사실 정다면체는 다섯 가지밖에 없다. | ||
{| class="wikitable" style="background:white;" width="100%" | {| class="wikitable" style="background:white;" width="100%" | ||
! 3차원 이미지 | ! 3차원 이미지 | ||
| 65번째 줄: | 65번째 줄: | ||
정다면체는 평면그래프이므로, 정다면체의 꼭지점의 개수, 모서리의 개수, 면의 개수를 각각 <math>v,e,f</math>라 하면 <math>v-e+f=2</math>이다([[오일러의 정리]]). 한편 그래프의 꼭짓점의 차수를 ''d''라고 하면 모든 꼭짓점의 차수의 합이 모서리의 수의 두 배이므로 <math>vd=2e</math>이고 정다면체를 이루는 정다각형이 ''n''다각형이면 <math>nf=2e</math>이다. 식을 잘 조작하면 | 정다면체는 평면그래프이므로, 정다면체의 꼭지점의 개수, 모서리의 개수, 면의 개수를 각각 <math>v,e,f</math>라 하면 <math>v-e+f=2</math>이다([[오일러의 정리]]). 한편 그래프의 꼭짓점의 차수를 ''d''라고 하면 모든 꼭짓점의 차수의 합이 모서리의 수의 두 배이므로 <math>vd=2e</math>이고 정다면체를 이루는 정다각형이 ''n''다각형이면 <math>nf=2e</math>이다. 식을 잘 조작하면 | ||
: <math>\frac{1}{d}+\frac{1}{n}=\frac{1}{e}+\frac{1}{2}</math> | : <math>\frac{1}{d}+\frac{1}{n}=\frac{1}{e}+\frac{1}{2}</math> | ||
을 얻는다. 한편 <math>n\ge 3, d\ge 3</math>이면서 동시에 <math>\frac{1}{d}+\frac{1}{n}> \frac{1}{2}</math>이어야 하므로 ''d''와 ''n'' 둘 모두 6보다 작다. | |||
* <math>n=3</math>일 때, <math>\frac{1}{d}-\frac{1}{e}=\frac{1}{6}</math>을 만족하는 (''d'',''e'')는 <math>(3,6),(4,12),(5,30)</math>이다. | * <math>n=3</math>일 때, <math>\frac{1}{d}-\frac{1}{e}=\frac{1}{6}</math>을 만족하는 (''d'',''e'')는 <math>(3,6),(4,12),(5,30)</math>이다. | ||
* <math>n=4</math>일 때, <math>\frac{1}{d}-\frac{1}{e}=\frac{1}{4}</math>을 만족하는 (''d'',''e'')는 <math>(3,12)</math>이다. | * <math>n=4</math>일 때, <math>\frac{1}{d}-\frac{1}{e}=\frac{1}{4}</math>을 만족하는 (''d'',''e'')는 <math>(3,12)</math>이다. | ||
2015년 5월 11일 (월) 15:40 판
정의
정다면체(Regular polyhedron)는 도형을 구성하는 면이 모두 합동인 다면체다. 플라톤의 입체(Platonic solid)라고도 한다. 정다면체는 다음과 같은 성질을 가진다.
- 각 면을 둘러싸고 있는 모서리의 개수가 같다.
- 다면체에서 면을 하나 제거한 후 임의로 조작하면 평면그래프를 얻을 수 있다. 그러면 그 그래프의 면은 원래 다면체의 면의 수와 동일하다.
- 꼭짓점과 연결된 변의 개수는 동일하다. 그래프로 간주하면, 각 꼭짓점의 차수는 모두 같다.
종류
사실 정다면체는 다섯 가지밖에 없다.
| 3차원 이미지 | 그래프 이미지 | 이름 | 면의 모양 | 꼭지점의 수 | 모서리의 수 | 면의 수 | 꼭지점의 차수 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|

|
정사면체 | 삼각형 | 4 | 6 | 4 | 3 |
|

|
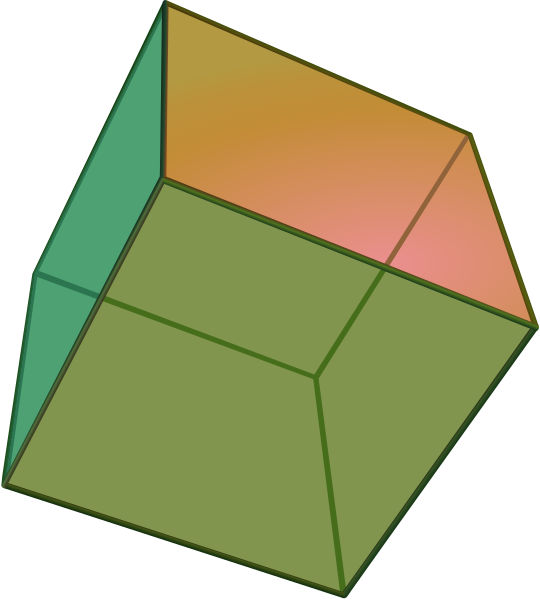
정육면체 | 사각형 | 8 | 12 | 6 | 3 |
|

|
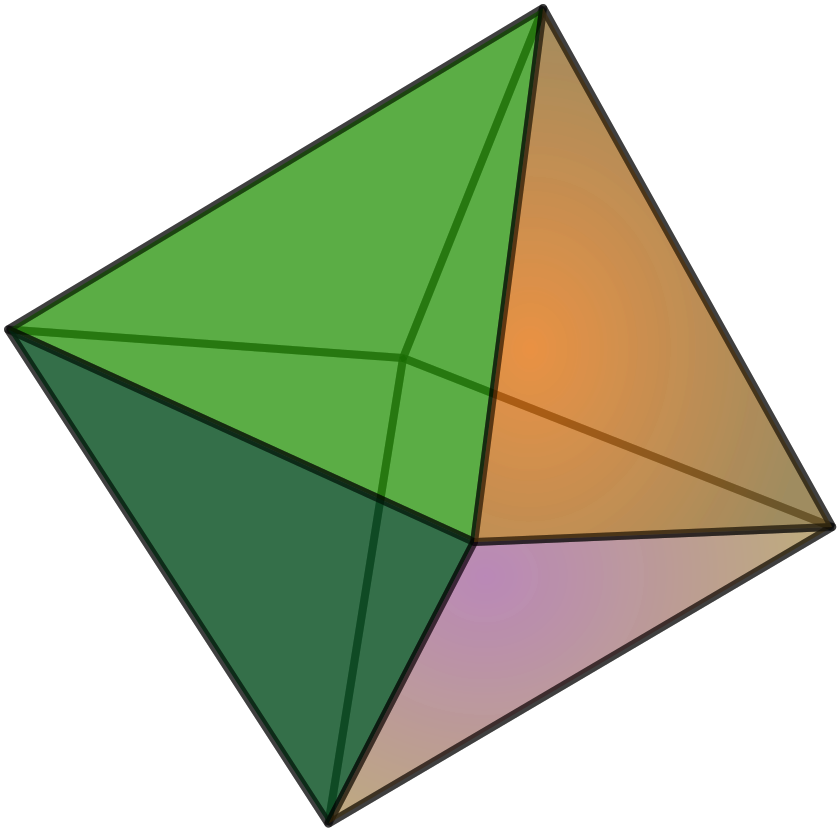
정팔면체 | 삼각형 | 6 | 12 | 8 | 4 |

|

|
정십이면체 | 오각형 | 20 | 30 | 12 | 3 |

|

|
정이십면체 | 삼각형 | 12 | 30 | 20 | 5 |
정다면체는 평면그래프이므로, 정다면체의 꼭지점의 개수, 모서리의 개수, 면의 개수를 각각 [math]\displaystyle{ v,e,f }[/math]라 하면 [math]\displaystyle{ v-e+f=2 }[/math]이다(오일러의 정리). 한편 그래프의 꼭짓점의 차수를 d라고 하면 모든 꼭짓점의 차수의 합이 모서리의 수의 두 배이므로 [math]\displaystyle{ vd=2e }[/math]이고 정다면체를 이루는 정다각형이 n다각형이면 [math]\displaystyle{ nf=2e }[/math]이다. 식을 잘 조작하면
- [math]\displaystyle{ \frac{1}{d}+\frac{1}{n}=\frac{1}{e}+\frac{1}{2} }[/math]
을 얻는다. 한편 [math]\displaystyle{ n\ge 3, d\ge 3 }[/math]이면서 동시에 [math]\displaystyle{ \frac{1}{d}+\frac{1}{n}\gt \frac{1}{2} }[/math]이어야 하므로 d와 n 둘 모두 6보다 작다.
- [math]\displaystyle{ n=3 }[/math]일 때, [math]\displaystyle{ \frac{1}{d}-\frac{1}{e}=\frac{1}{6} }[/math]을 만족하는 (d,e)는 [math]\displaystyle{ (3,6),(4,12),(5,30) }[/math]이다.
- [math]\displaystyle{ n=4 }[/math]일 때, [math]\displaystyle{ \frac{1}{d}-\frac{1}{e}=\frac{1}{4} }[/math]을 만족하는 (d,e)는 [math]\displaystyle{ (3,12) }[/math]이다.
- [math]\displaystyle{ n=5 }[/math]일 때, [math]\displaystyle{ \frac{1}{d}-\frac{1}{e}=\frac{3}{10} }[/math]을 만족하는 (d,e)는 [math]\displaystyle{ (3,30) }[/math]이다.
각 해에서 면의 수를 구하면 4, 8, 20, 6, 12이다.