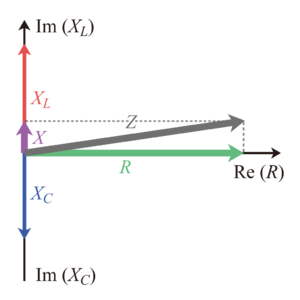
임피던스((electrical) impedance)는 교류 회로에서의 [math]\displaystyle{ V/I }[/math]를 말한다. RLC 회로에서, 코일(L)은 저항보다 위상이 [math]\displaystyle{ \pi/2 }[/math] 크게(빠르게), 축전기(C)는 [math]\displaystyle{ \pi/2 }[/math] 작게(느리게) 나타나며, 이를 복소수로 나타낸 것을 복소 임피던스(complex impedance)라 한다.
리액턴스[편집 | 원본 편집]
RLC 회로에서 코일과 축전기는 각각 전류의 흐름을 방해하는 저항의 작용을 하며[1], 이를 수치로 나타낸 것이 리액턴스(reactance)이다. 코일의 리액턴스는 유도 리액턴스(inductive reactance) [math]\displaystyle{ X_L }[/math], 축전기의 리액턴스는 용량 리액턴스(capacitive reactance) [math]\displaystyle{ X_C }[/math]라 부른다. 이 둘의 정의는 다음과 같다.
- [math]\displaystyle{ X_L := \omega L = 2\pi f L }[/math]
- [math]\displaystyle{ X_C := \frac{1}{\omega C} = \frac{1}{2\pi f C} }[/math]
여기서 [math]\displaystyle{ f }[/math]는 교류 전원의 진동수를, [math]\displaystyle{ \omega }[/math]는 교류 전원의 각진동수를, [math]\displaystyle{ L }[/math]은 코일의 (자체)유도계수를, [math]\displaystyle{ C }[/math]는 축전기의 전기 용량을 뜻한다.
복소 임피던스[편집 | 원본 편집]
복소 임피던스를 다음과 같이 정의한다.
- [math]\displaystyle{ Z := Z_R + Z_L + Z_C = R+(j\omega) L + \frac{1}{(j\omega) C} = R+jX = R+j(X_L - X_C) }[/math]
여기서 임피던스 [math]\displaystyle{ |Z| }[/math]를 이 크기로 정의한다.
- [math]\displaystyle{ |Z| = | R+j(X_L - X_C)| = \sqrt{R^2 + (X_L - X_C)^2} }[/math]
공진 주파수[편집 | 원본 편집]
공진 주파수(공진 진동수, resonant frequency, resonance freq.)는 전류가 가장 클 때의 주파수로, 임피던스를 이용하여 구할 수 있다. [math]\displaystyle{ I=\frac{V}{|Z|} }[/math]가 최대이므로 [math]\displaystyle{ V }[/math]가 일정할 때 [math]\displaystyle{ |Z|=\sqrt{R^2 + (X_L - X_C)^2} }[/math]가 최소여야 한다. 즉 [math]\displaystyle{ X_L = X_C }[/math], 풀어 말하면
- [math]\displaystyle{ 2\pi f L = \frac{1}{2\pi f C}, \; \; f = \frac{1}{2\pi \sqrt{LC}} }[/math]
일 때 전류가 최대이다. 이때의 주파수 [math]\displaystyle{ f_0 = \frac{1}{2\pi \sqrt{LC}} }[/math]가 공진 주파수이다.
- ↑ 코일의 경우에는 유도기전력이 전류를 방해하고, 축전기의 경우에는 전하들 사이의 전자기적 상호작용(인력·반발력)이 전류를 방해한다.