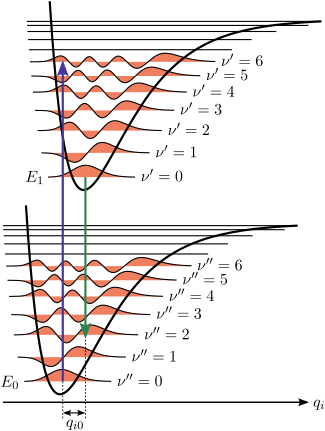
Figure 1. Franck–Condon principle energy diagram. Since electronic transitions are very fast compared with nuclear motions, vibrational levels are favored when they correspond to a minimal change in the nuclear coordinates. The potential wells are shown favoring transitions between v = 0 and v = 2.
프랑크–콘돈 원리란 분광학과 양자화학에서 진동전자 전이(vibronic transition)의 세기를 설명하는 법칙이다. 진동전자 전이란 분자가 광자를 흡수 또는 방출하여 진동에너지 준위와 전자 에너지준위가 동시에 변하는 것을 말한다. 원리는 전자 전이가 일어나는 동안 진동 에너지 준위의 변화는 두 진동 파동함수가 더 많이 중첩되는 것으로 일어난다는 것이다.
개관

Figure 2. Schematic representation of the absorption and fluorescence spectra corresponding to the energy diagram in Figure 1. The symmetry is due to the equal shape of the ground and excited state potential wells. The narrow lines can usually only be observed in the spectra of dilute gases. The darker curves represent the inhomogeneous broadening of the same transitions as occurs in liquids and solids. Electronic transitions between the lowest vibrational levels of the electronic states (the 0–0 transition) have the same energy in both absorption and fluorescence.

Figure 3. Semiclassical pendulum analogy of the Franck-Condon principle. Vibronic transitions are allowed at the classical turning points because both the momentum and the nuclear coordinates correspond in the two represented energy levels. In this illustration, the 0–2 vibrational transitions are favored.
전자 전이에 필요한 시간(1 펨토초)은 진도의 1주기 시간(100 펨토초)에 비해 매우 짧다. 고로 이 기간 내에 결합 간격 및 핵의 운동 에너지는 거의 변동이 없고 그 상태를 유지하면서 전자 전이를 한다.
제임스 프랑크 [Franck 1926]가 처음 반(半)고전역학적인 방법으로 설명했다. 전자전이는 핵 운동에 비해 훨씬 빠르게 일어나므로, 전자 전이가 일어나 분자가 새로운 진동 준위로 옮겨갈 때 새로운 진동 준위는 원래 원자의 위치와 운동량이 맞아야 한다.
 이 문서에는 영어판 위키백과의 Franck–Condon principle 문서를 번역한 내용이 포함되어 있습니다.
이 문서에는 영어판 위키백과의 Franck–Condon principle 문서를 번역한 내용이 포함되어 있습니다.